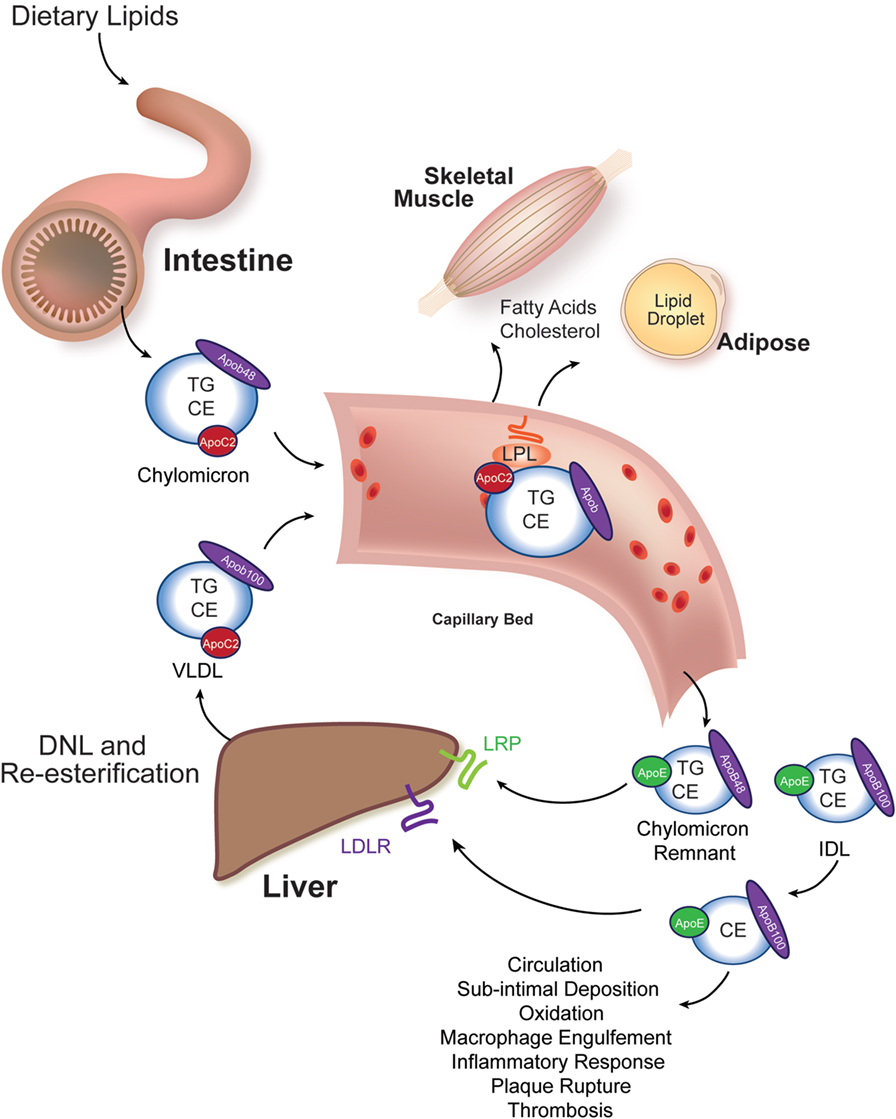
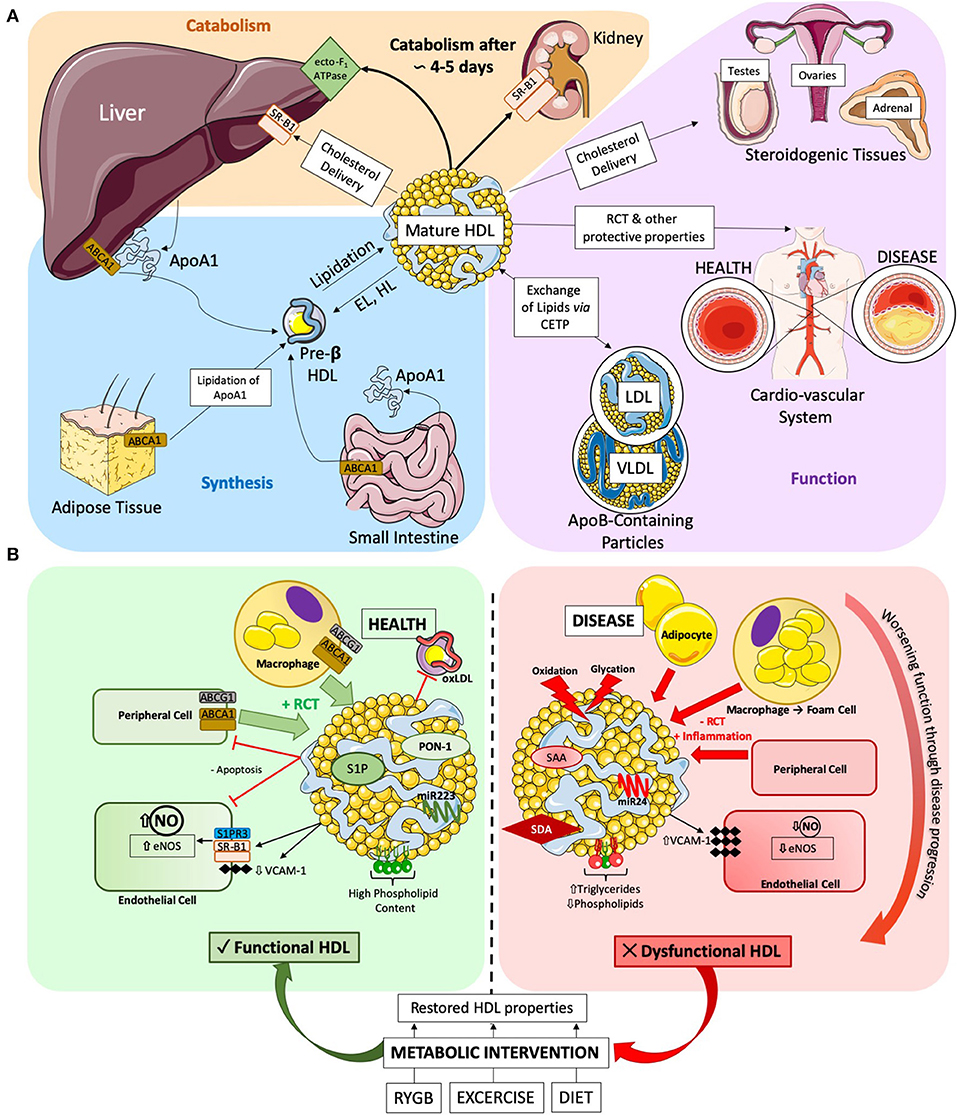
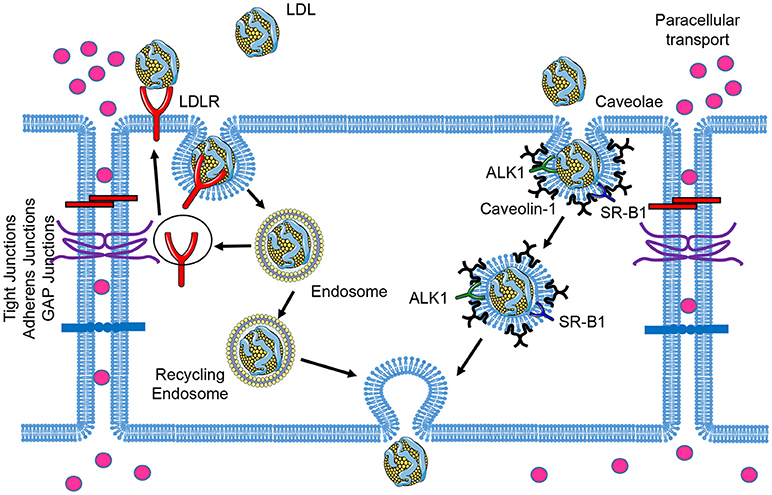
Lipoprotein(a): A Genetically Determined, Causal, and Prevalent Risk Factor for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association | Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology

Glycated Apolipoprotein A-IV Induces Atherogenesis in Patients With CAD in Type 2 Diabetes - ScienceDirect
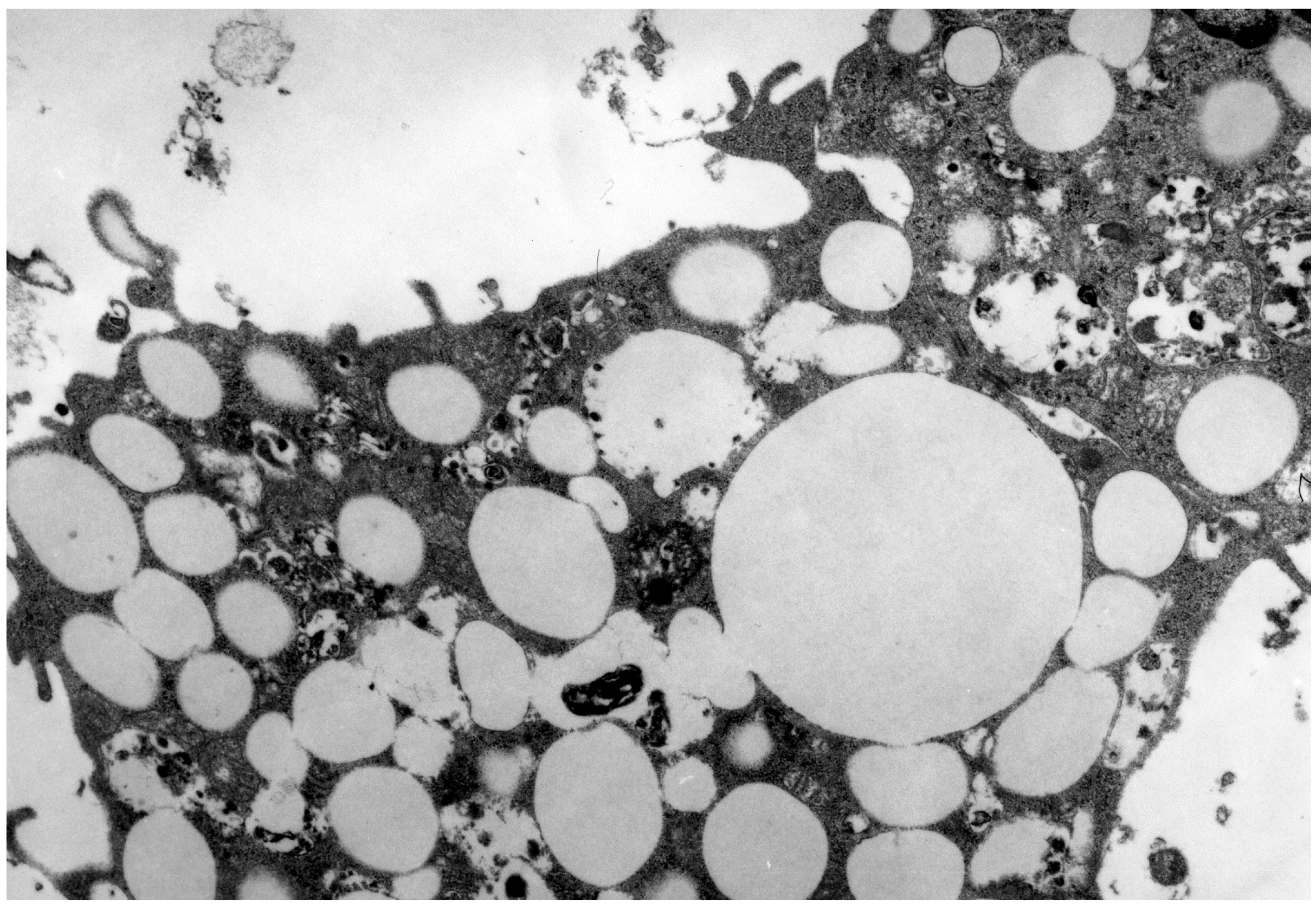
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Modified Low Density Lipoprotein and Lipoprotein-Containing Circulating Immune Complexes as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers of Atherosclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Macrovascular Disease

Lipoprotein(a) and Cardiovascular Disease in Chinese Population: A Beijing Heart Society Expert Scientific Statement | JACC: Asia

Glycated apolipoprotein B decreases after bariatric surgery in people with and without diabetes: A potential contribution to reduction in cardiovascular risk - ScienceDirect
Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Show Altered Lipoprotein Profiles with Dysfunctional High-Density Lipoproteins that Can Exacerbate Inflammatory and Atherogenic Process | PLOS ONE
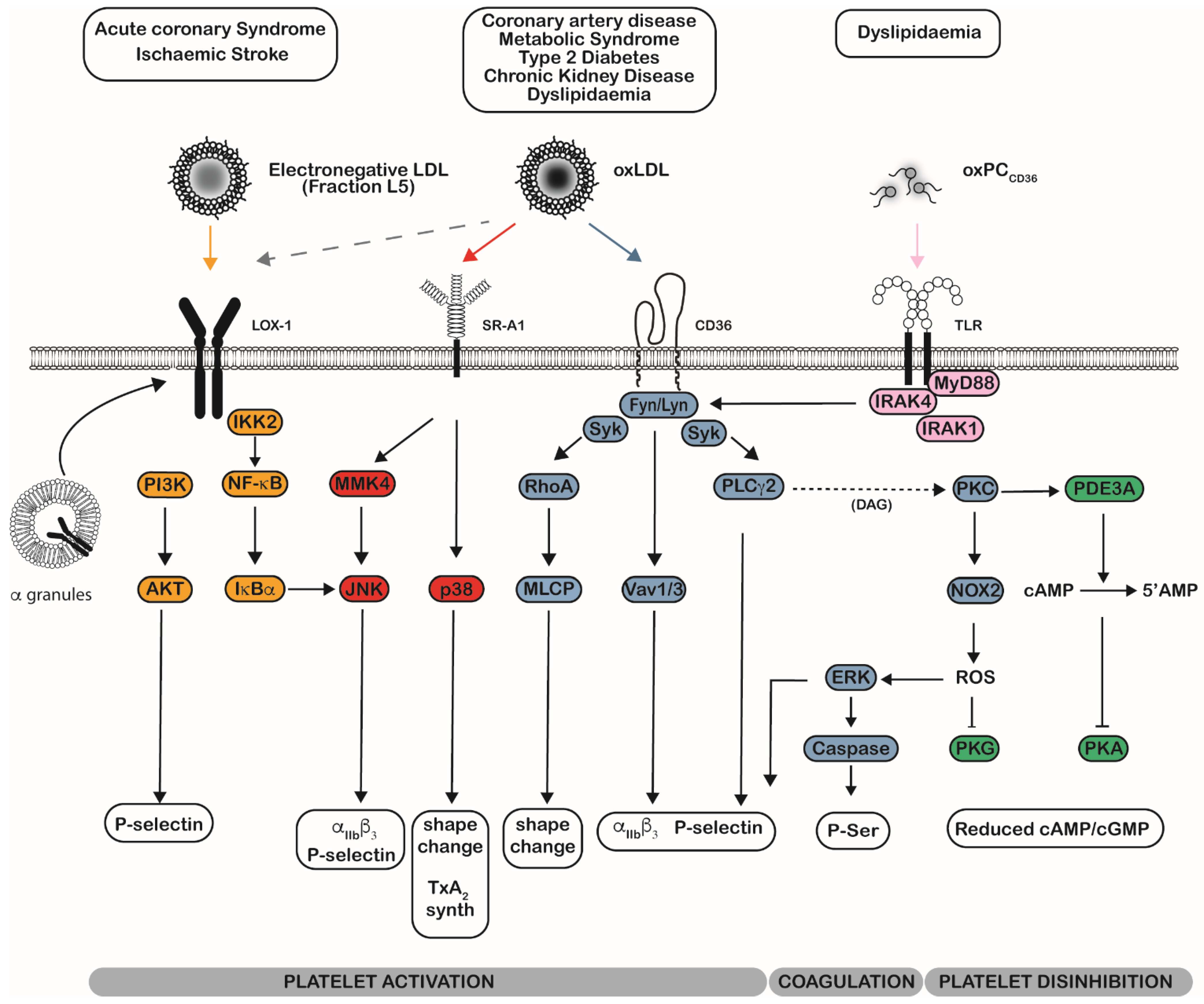
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Oxidised Low-Density Lipoprotein-Induced Platelet Hyperactivity—Receptors and Signalling Mechanisms
![Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] shows maximum internalization at 2 h in human... | Download Scientific Diagram Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] shows maximum internalization at 2 h in human... | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316226017/figure/fig1/AS:484621214326784@1492554109404/Lipoproteina-Lpa-shows-maximum-internalization-at-2-h-in-human-hepatoma-HepG2.png)
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] shows maximum internalization at 2 h in human... | Download Scientific Diagram
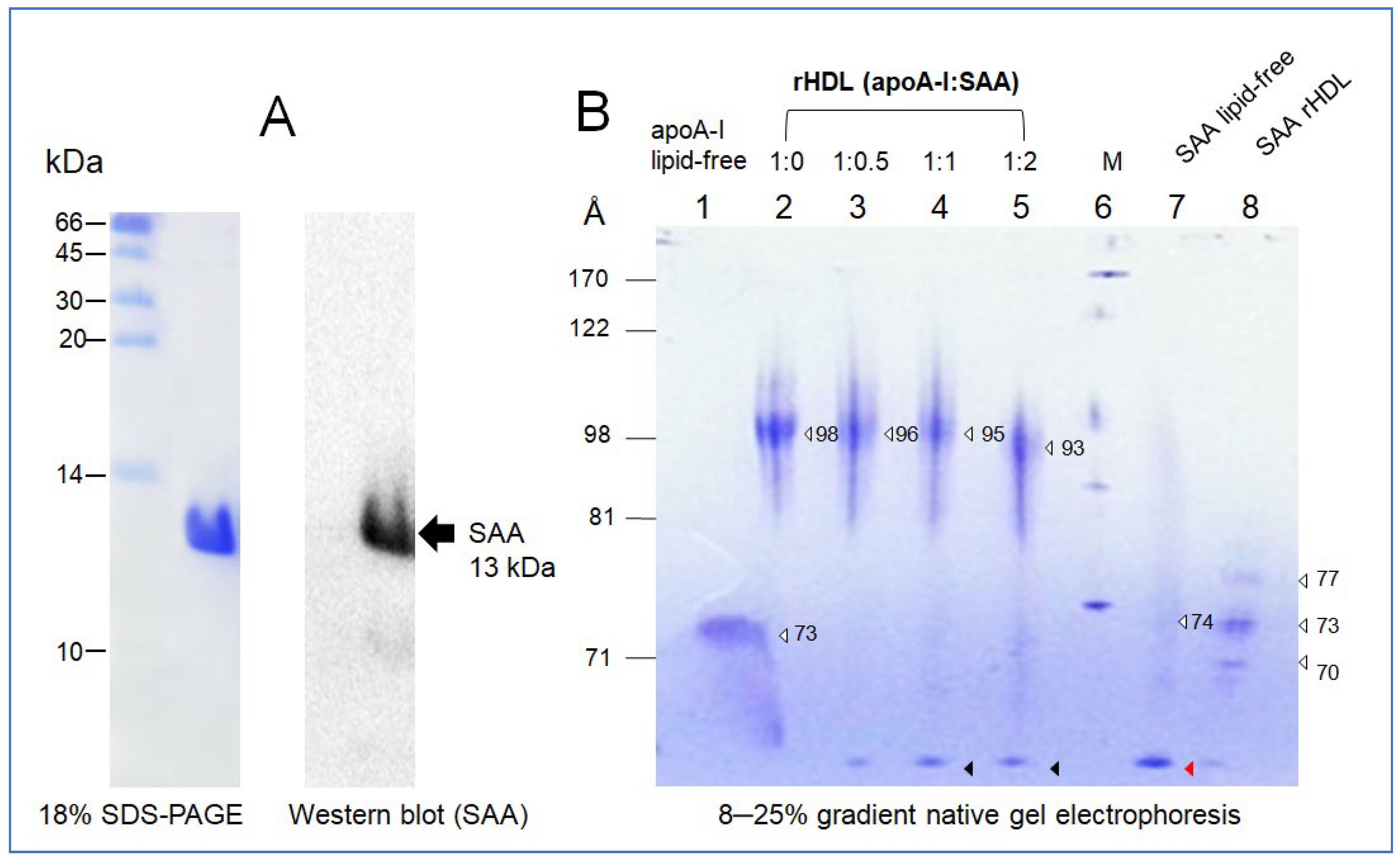
Molecules | Free Full-Text | Human Serum Amyloid a Impaired Structural Stability of High-Density Lipoproteins (HDL) and Apolipoprotein (Apo) A-I and Exacerbated Glycation Susceptibility of ApoA-I and HDL

Frontiers | Pathological Crosstalk Between Oxidized LDL and ER Stress in Human Diseases: A Comprehensive Review

Phase contrast microscope image of cells treated with glycated BSA.... | Download Scientific Diagram

Effect of crocin on glycated human low-density lipoprotein: A protective and mechanistic approach - ScienceDirect

Modulating Lipoprotein Transcellular Transport and Atherosclerotic Plaque Formation in ApoE–/– Mice via Nanoformulated Lipid–Methotrexate Conjugates | ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces

Effects of triacylglycerol on the structural remodeling of human plasma very low- and low-density lipoproteins - ScienceDirect

Arginine-directed glycation and decreased HDL plasma concentration and functionality | Nutrition & Diabetes

Molecules | Free Full-Text | Structural and Functional Impairments of Reconstituted High-Density Lipoprotein by Incorporation of Recombinant β-Amyloid42